
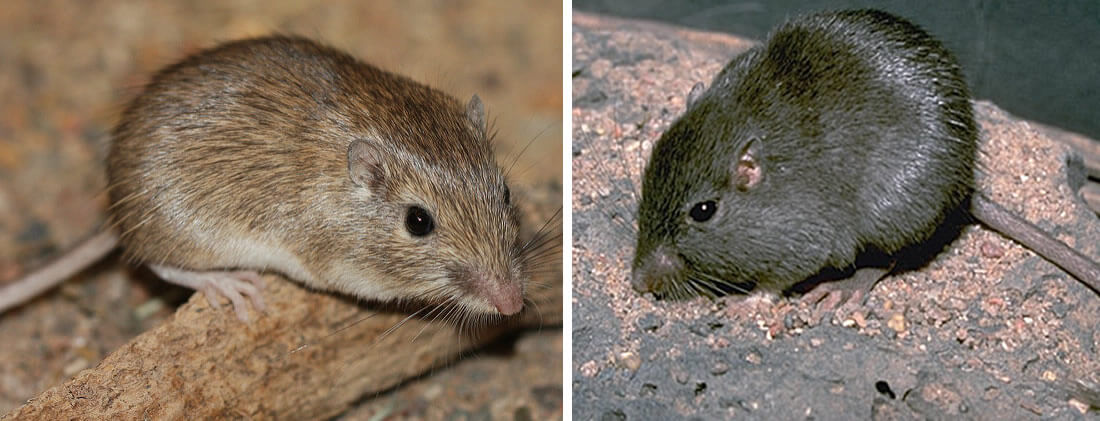
They have been observed plugging the entrance to their burrows, which may serve to retain They stay in cool undergroundīurrows during the day. Their kidneys highly concentrate waste, resulting in very viscous urine. Rock pocket mice, found throughout the southwestern United States, are well adapted to their dry, rocky, desertĮnvironment. Much like a mouse, pocket mice are more closely related to pocket gophers than to true mice. The rock pocket mouse (Chaetodipus intermedius) is a small rodent in the Heteromyidae family. Random, but natural selection is not random.ĭifferent mutations can cause the same phenotype.Įvolution repeats itself in different environments. Mutations that increase the fitness of an organismĮvolution is not a random process. A small advantageĬan lead to change in the population very quickly. In dark environments, the dark colored mice haveĪn advantage they survive better and have moreĮvolution can happen quickly. Mutations in the Mc1r gene, which controls theĪmount of dark pigment in a mouse’s hair follicles, Mutations are favored, rejected, or neutralĭepending upon an organism’s environment. The differences in mouse fur color are driven by To be dark the predators come from above. The mice’s underbelliesĪre white because there’s so selective pressure for it The top of their bodies, providing camouflage so Mice in the darker environment have darker fur on Mexico’s desert: lighter sands and darker lava rock. Pocket mice live in different environments in New Suggested pause points, indicating the beginning and end times in minutes in the film. The film may be viewed in its entirety or paused at specific points to review content with students.

Rock pocket mouse worksheet answer key code#
know what a gene is and that genes can code for proteins that determine traits and.have a basic understanding of what a food web is and that organisms fill specific niches in their environments.have a basic understanding of natural selection, evolution, and adaptation.This means that other organisms in theĮnvironment (in this case, the predators) can be a selective force.įriedland, Relyea, and CourardHauri, Environmental Science for AP* Selective pressure depends on the environment in which an organism lives. While mutations can be random, natural selection is not random. Different mutations in the same gene, or even mutations in different genes, can result in the same phenotype.į. Evolution can happen quickly (in hundreds of years, or even less) advantageous genetic mutations can increase inįrequency in a population quite rapidly, even if the fitness advantage to the organism is small.Į. Mutations that increase the fitness of an organism increase in frequency in a population.ĭ. The environment contributes to determining whether a mutation is advantageous, deleterious, or neutral.Ĭ. A mutation is a random change to an organism’s DNA sequence.ī. Michael Nachman, working in the field and lab, has quantified predation on rock pocket miceĪnd identified adaptive changes in coat-color genes that allow the mice to travel under the radar of hungry predators.Ī. Evolution is happening right now, everywhere around us, and adaptive changes can sweep through a population in anĮvolutionary eyeblink.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
